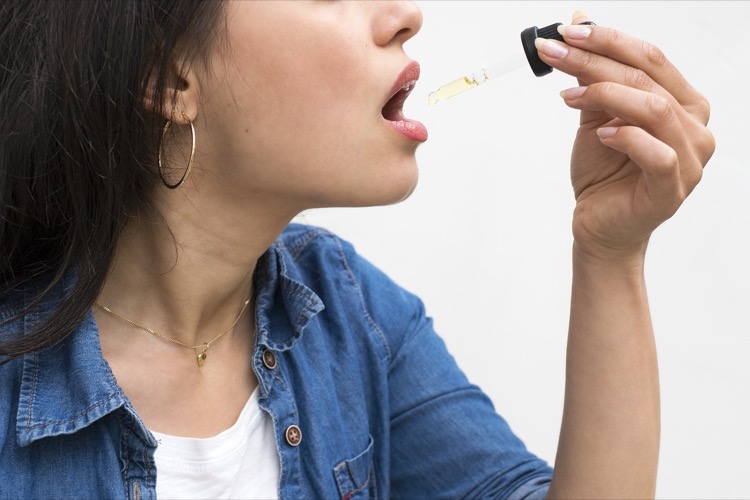
CBD, or cannabidiol, is one of the many active compounds that are contained in hemp seed (Cannabis sativa). These compounds are cannabinoids. Cannabidiol (or CBD) is extracted from the inflorescence of the cannabis sativa plant, so by sourcing the CBD oilsIt is always worth reading the composition. It is often the case that hemp seed oil is called CBD oil, but in fact it does not contain CBD.
Unlike THC, which is an ingredient in marijuana, CBD is not psychoactiveIt rarely has side effects when consumed and they are not too troublesome. It is neither addictive nor intoxicating. However, the list of positive effects of CBD oils on the body is impressive.
What is the endocannabinoid system and how does it work
To understand the effects of CBD on the body, one must start with one of the systems found in the human body. This is endocannobinoid system. Discovered relatively recently, only in the 1990s. It is an overarching system that acts as a regulatory network for the most important biological processes in the human body.
It's all a bit convoluted and there are still more questions than answers, and the research is still ongoing and we will be surprised by many things. One thing is already known, however: the endocannabinoid system has a huge impact on the proper functioning of other systems in the human body. And they all form a network of interdependencies through which the body works like a good watch. If the endocannabonoid system is working properly, the human body maintains homeostasis (balance), i.e. the body's ability to self-regulate biological processes.
When, as a result of some dysfunction of the endocannabinoid system, this balance (homeostasis) in the body is disturbed and the communication of individual systems begins to be disrupted, this becomes the starting point for the development of various diseases and illnesses.
- Cannabinoid receptorswhich are distributed throughout the body (it is the endocannabinoids that adhere to them).
- Endocannabinoids, which are neurotransmitters that support the body in regulating the endocannabinoid system and thus maintaining homeostasis in the body.
- Enzymes, which are responsible for the breakdown of endocannabinoids.
How CBD affects the body
There is no direct relationship between CBD and cannabinoid receptors, in any case that is what the research conducted so far suggests. But the compound has the power to increase the production of endocannabinoids in the human body and, just as importantly, has the effect of prolonging their availability to the body, as it blocks the enzymes responsible for metabolising endocannabinoids. This is particularly true of the FAAH enzyme.
One of these endocannabinoids is anandamide, which is otherwise known as human THC, due to its almost identical structure. It is also called the pleasure molecule. Studies indicate that its deficiencies are associated with migraines, recurrent anxiety, epilepsy or inflammatory conditions, among others.
Cannabidiol also exhibits adaptogenic effects, i.e. it first 'repairs' those functions of the endocannabinoid system that are most disturbed, only then dealing with modulating it so that the body returns to balance.
Therapeutic properties of CBD
Research into the properties of cannabidiol is still ongoing. And we will probably continue to be surprised by the possibilities of CBD. What is known today is extremely promising, as cannabidiol shows a whole range of positive effects on the human body. The most important ones are:
- Neuroactive i neuroprotective - Cannabidiol combats neurodegenerative disorders by regenerating nerve cells and stimulating the nervous system, and has a relaxing and anti-spastic effect.
- Antioxidant - influences the reduction of oxidative stress, slows down cell and tissue ageing, supports the body's natural defence mechanisms and protects against free radicals.
- Analgesic - relieves and also eliminates pain in the body. In the fight against pain, it can be used both externally and internally.
- Anti-inflammatory - inhibits and fights inflammation in the body and, when used prophylactically, prevents its formation.
- Antimicrobial - has strong anti-bacterial properties, preventing the proliferation of bacteria and their growth.
- Antifungal - kills mould and fungi and prevents the development of fungal diseases.
- Antiemetic - reduces nausea and vomiting, which is extremely helpful, especially for cancer patients who are receiving chemotherapy.
- Stimulating thirst and appetiteand at the same time influences the body's normal metabolism.
- Antipsychotic - has the ability to alleviate anxiety and psychosis, has a calming and tranquilising effect, and relaxes. At the same time, it facilitates falling asleep and ensures a good night's sleep.
- Anti-allergic - alleviates or even eliminates allergy symptoms, regardless of the cause.
- Dermatological - soothes skin irritations and fights skin diseases, accelerates wound healing and rejuvenates the epidermis.
- Immunological - supports the body's natural immunity, strives to ensure a state of homeostasis,
- Anti-cancer - Research into this aspect of the effects is still ongoing, but the results are promising. It appears that CBD inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells and even contributes to their annihilation.